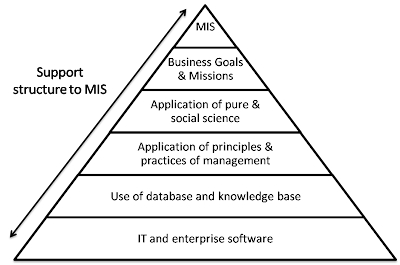
The concept is a blend of principles, theories and practices of management, information and system giving rise to a single product called MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
The concept of management gives high regard to the individual and his ability to use the information. MIS gives information through data analysis. While analyzing the information, it relies on many academic disciplines like management science, OR, organization behavior, psychology, etc.
The foundation of MIS is the principles of management and its practices. MIS uses the concept of management control in its design and relies heavily on the fact that the decision maker is a human being and is a human processor of information.
A MIS can be evolved for a specific objective it is evolved after systematic planning and design. It calls for an analysis of business, management views and policies, organization culture and the management style.
The MIS,therefore relies heavily on systems theory.The systems theory offers solutions to handle complex situations of the input and output flows. it uses theory of communication which helps to evolve a system design capable of handling data inputs, process, the outputs with the least possible noise or distortion in transmitting the information from a source to destination.
Comments